
Call 1800-123-2003

"Smartindia is the best online tool for school students." Ms Deepa Chandran, Principal Anchal
"Smartindia is one of the best supplementary education tool for school students." Ms Pooja, Principal
want a brief on gauss's law ,proof and application |
|||||
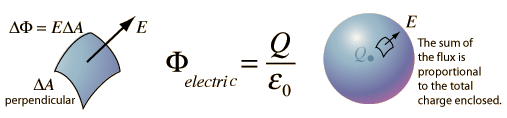 Gauss' law is a powerful tool for the calculation of electric fields when they originate from charge distributions of sufficient symmetry to apply it. 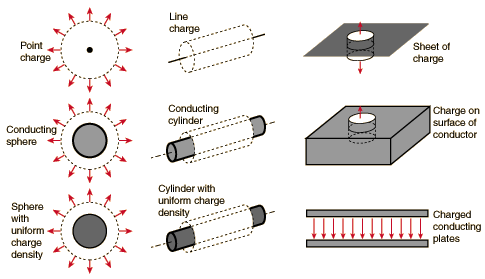
If the charge distribution lacks sufficient symmetry for the application of Gauss' law, then the field must be found by summing the point charge fields of individual charge elements. Examples are:
|
