Welcome to Smartindia Student's Blogall posts
Helium
Helium-4 (4
2He or 4He) is a non-radioactive isotope of the element helium. It is by far the most abundant of the two naturally occurring isotopes of helium, making up about 99.99986% of the helium on Earth. Its nucleus is identical to an alpha particle, and consists of two protons and two neutrons.
sulphur dioxide
sulphur dioxide) is the chemical compound with the formula SO
2. At standard atmosphere, it is ea toxic gas with a pungent, irritating, and rotten smell. Thetriple point is 197.69 K and 1.67kPa. It is released naturally by volcanic activity.
Sulfur dioxide was used by the Romans in winemaking, when they discovered that burning sulfur candles inside empty wine vessels kept them fresh and free from vinegar smell
washington DC
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to asWashington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. The signing of the Residence Act on July 16, 1790, approved the creation of a capital district located along the Potomac River on the country's East Coast. The U.S. Constitution provided for a federal district under the exclusive jurisdiction of theCongress and the District is therefore not a part of any U.S. state.
delhi
Delhi (/?d?li/, Hindustani pronunciation: [d??lli?] Dilli ), also known as the National Capital Territory of India is a metropolitan region in India. Such is the nature of urban expansion in India that its growth has expanded beyond the NCT to incorporate towns in neighbouring states and at its largest extent can count a population of nearly 27 million residents as of 2014,[3] and is the largest urban agglomeration in India by land area and population. It is also the 2nd most populous city on the planet.[4][5] The NCT and its urban region have been given the special status of National Capital Region(NCR) under the Constitution of India's 69th amendment act of 1991. The NCR includes the neighbouring cities of Gurgaon, Noida, Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Greater Noida, Sonepat, Panipat, Karnal, Rohtak, Rewari, Baghpat, Meerut, Alwar, Bharatpurand other nearby towns.
hertz
The hertz (symbol Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as one cycle per second.[1] One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications, such as the frequency of musical tones. The unit is named for Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, who was the first to conclusively prove the existence of electromagnetic waves.
england
England ![]() i/????l?nd/ is a country that is part of the United Kingdom.[2][3][4] It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west. The Irish Sea lies north west of England, whilst the Celtic Sea lies to the southwest. The North Sea to the east and theEnglish Channel to the south separate it from continental Europe. Most of England comprises the central and southern part of the island of Great Britain which lies in theNorth Atlantic. The country also includes over 100 smaller islands such as the Isles of Scilly, and the Isle of Wight.
i/????l?nd/ is a country that is part of the United Kingdom.[2][3][4] It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west. The Irish Sea lies north west of England, whilst the Celtic Sea lies to the southwest. The North Sea to the east and theEnglish Channel to the south separate it from continental Europe. Most of England comprises the central and southern part of the island of Great Britain which lies in theNorth Atlantic. The country also includes over 100 smaller islands such as the Isles of Scilly, and the Isle of Wight.
Mexico
Mexico (![]() i/?m?ks?ko?/; Spanish: México [?mexiko] (
i/?m?ks?ko?/; Spanish: México [?mexiko] (![]() )), officially the United Mexican States (Spanish:
)), officially the United Mexican States (Spanish: ![]() Estados Unidos Mexicanos (help·info)),[9][10][11][12] is afederal republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and theCaribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of Mexico.[13] Covering almost two million square kilometres (over 760,000 sq mi),[12] Mexico is the fifth largest country in theAmericas by total area and the 13th largest independent nation in the world. With an estimated population of over 113 million,[14] it is the eleventh most populous and the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world and the second most populous country in Latin America. Mexico is a federation comprising thirty-one states and a Federal District, the capital city.
Estados Unidos Mexicanos (help·info)),[9][10][11][12] is afederal republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and theCaribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of Mexico.[13] Covering almost two million square kilometres (over 760,000 sq mi),[12] Mexico is the fifth largest country in theAmericas by total area and the 13th largest independent nation in the world. With an estimated population of over 113 million,[14] it is the eleventh most populous and the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world and the second most populous country in Latin America. Mexico is a federation comprising thirty-one states and a Federal District, the capital city.
(/?tæm?l ?n??du?/ tam-il-nah-doo;About this sound Tamil pronunciation (help·info); literallyThe Land
Tamil Nadu (/?tæm?l ?n??du?/ tam-il-nah-doo;![]() Tamil pronunciation (help·info); literallyThe Land of Tamils or Tamil Country) is one of the 29 states of India. Its capital isChennai (formerly known as Madras), the largest city. Tamil Nadu[6] lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory ofPuducherry and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh. It is bounded by the Eastern Ghats on the north, by the Nilgiri, the Anamalai Hills, and Kerala on the west, by the Bay of Bengal in the east, by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait on the southeast, and by the Indian Ocean on the south.
Tamil pronunciation (help·info); literallyThe Land of Tamils or Tamil Country) is one of the 29 states of India. Its capital isChennai (formerly known as Madras), the largest city. Tamil Nadu[6] lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory ofPuducherry and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh. It is bounded by the Eastern Ghats on the north, by the Nilgiri, the Anamalai Hills, and Kerala on the west, by the Bay of Bengal in the east, by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait on the southeast, and by the Indian Ocean on the south.
X-radiation
X-radiation (composed of X-rays) is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz (3×1016Hz to 3×1019 Hz) and energies in the range 100 eV to 100 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to with terms meaning Röntgen radiation, after Wilhelm Röntgen,[1] who is usually credited as its discoverer, and who had named it X-radiation to signify an unknown type of radiation.[2] Spelling of X-ray(s) in the English language includes the variants x-ray(s), xray(s) and X ray(s)
Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea is the name given to the northern part of the East China Sea, which is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It is located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula. Its name comes from the sand particles from Gobi Desert sand storms that turn the surface of the water golden yellow.
The innermost bay of the Yellow Sea is called the Bohai Sea (previously Pechihli Bay or Chihli Bay). Into it flow both the Yellow River (through Shandong province and its capital Jinan) and Ha i He (through Beijing and Tianjin). Deposits of sand and silt from those rivers contribute to the sea color.
The Yellow Sea is one of four seas named in English after common color terms — the others being the Black Sea, the Red Sea and the White Sea.
sources of light
There are many sources of light. The most common light sources are thermal: a body at a giventemperature emits a characteristic spectrum of black-body radiation. A simple thermal source issunlight, the radiation emitted by the chromosphere of the Sun at around 6,000 Kelvin peaks in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum when plotted in wavelength units [17] and roughly 44% of sunlight energy that reaches the ground is visible.[18] Another example isincandescent light bulbs, which emit only around 10% of their energy as visible light and the remainder as infrared. A common thermal light source in history is the glowing solid particles inflames, but these also emit most of their radiation in the infrared, and only a fraction in the visible spectrum. The peak of the blackbody spectrum is in the deep infrared, at about 10 micrometer wavelength, for relatively cool objects like human beings. As the temperature increases, the peak shifts to shorter wavelengths, producing first a red glow, then a white one, and finally a blue-white colour as the peak moves out of the visible part of the spectrum and into the ultraviolet. These colours can be seen when metal isheated to "red hot" or "white hot". Blue-white thermal emission is not often seen, except in stars (the commonly seen pure-blue colour in a gas flame or a welder's torch is in fact due to molecular emission, notably by CH radicals (emitting a wavelength band around 425 nm, and is not seen in stars or pure thermal radiation).
refraction
Refraction is the bending of light rays when passing through a surface between one transparent material and another. It is described by Snell's Law:
where 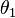 is the angle between the ray and the surface normal in the first medium,
is the angle between the ray and the surface normal in the first medium, 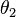 is the angle between the ray and the surface normal in the second medium, and n1 and n2 are the indices of refraction, n = 1 in a vacuum and n > 1 in a transparent substance.
is the angle between the ray and the surface normal in the second medium, and n1 and n2 are the indices of refraction, n = 1 in a vacuum and n > 1 in a transparent substance.
When a beam of light crosses the boundary between a vacuum and another medium, or between two different media, the wavelength of the light changes, but the frequency remains constant. If the beam of light is not orthogonal (or rather normal) to the boundary, the change in wavelength results in a change in the direction of the beam. This change of direction is known as refraction.
The refractive quality of lenses is frequently used to manipulate light in order to change the apparent size of images. Magnifying glasses, spectacles, contact lenses, microscopes and refracting telescopes are all examples of this manipulation.