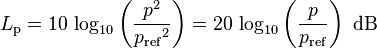Welcome to Smartindia Student's Blogall posts
light
Light is radiant energy, usually referring to electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight.[1] Visible light is usually defined as having a wavelength in the range of 400 nanometres (nm), or 400×10?9 m, to 700 nanometres – between the infrared, with longer wavelengths and the ultraviolet, with shorter wavelengths.[2][3] These numbers do not represent the absolute limits of human vision, but the approximate range within which most people can see reasonably well under most circumstances. Various sources define visible light as narrowly as 420 to 680[4][5] to as broadly as 380 to 800 nm.[6][7] Under ideal laboratory conditions, people can see infrared up to at least 1050 nm,[8] children and young adults ultraviolet down to about 310 to 313 nm
sound pressure
Sound pressure is the difference, in a given medium, between average local pressure and the pressure in the sound wave. A square of this difference (i.e., a square of the deviation from the equilibrium pressure) is usually averaged over time and/or space, and a square root of this average provides a root mean square (RMS) value. For example, 1 Pa RMS sound pressure (94 dBSPL) in atmospheric air implies that the actual pressure in the sound wave oscillates between (1 atm 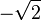 Pa) and (1 atm
Pa) and (1 atm  Pa), that is between 101323.6 and 101326.4 Pa. As the human ear can detect sounds with a wide range of amplitudes, sound pressure is often measured as a level on a logarithmic decibel scale. The sound pressure level (SPL) or Lp is defined as
Pa), that is between 101323.6 and 101326.4 Pa. As the human ear can detect sounds with a wide range of amplitudes, sound pressure is often measured as a level on a logarithmic decibel scale. The sound pressure level (SPL) or Lp is defined as
- where p is the root-mean-square sound pressure and
 is a reference sound pressure. Commonly used reference sound pressures, defined in the standard ANSI S1.1-1994, are 20µPa in air and 1 µPa in water. Without a specified reference sound pressure, a value expressed in decibels cannot represent a sound pressure level.
is a reference sound pressure. Commonly used reference sound pressures, defined in the standard ANSI S1.1-1994, are 20µPa in air and 1 µPa in water. Without a specified reference sound pressure, a value expressed in decibels cannot represent a sound pressure level.
Since the human ear does not have a flat spectral response, sound pressures are often frequencyweighted so that the measured level matches perceived levels more closely. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has defined several weighting schemes. A-weighting attempts to match the response of the human ear to noise and A-weighted sound pressure levels are labeled dBA. C-weighting is used to measure peak levels.
sound waves
Sound waves are often simplified to a description in terms of sinusoidal plane waves, which are characterized by these generic properties:
- Frequency, or its inverse, the period
- Wavelength
- Wave number
- Amplitude
- Sound pressure
- Sound intensity
- Speed of sound
- Direction
sound
Sound can propagate through compressible media such as air, water and solids as longitudinal waves and also as a transverse waves in solids (see Longitudinal and transverse waves, below). The sound waves are generated by a sound source, such as the vibrating diaphragm of a stereo speaker. The sound source creates vibrations in the surrounding medium. As the source continues to vibrate the medium, the vibrations propagate away from the source at the speed of sound, thus forming the sound wave. At a fixed distance from the source, the pressure, velocity, and displacement of the medium vary in time. At an instant in time, the pressure, velocity, and displacement vary in space. Note that the particles of the medium do not travel with the sound wave. This is intuitively obvious for a solid, and the same is true for liquids and gases (that is, the vibrations of particles in the gas or liquid transport the vibrations, while the average position of the particles over time does not change). During propagation, waves can be reflected,refracted, or attenuated by the medium
USA
The United States of America (USA or U.S.A.), commonly referred to as the United States (US or U.S.), America, and sometimes the States, is a federal republic[17][18]consisting of 50 states and a federal district. The 48 contiguous states and Washington, D.C., are in central North America between Canada and Mexico. The state of Alaska is the northwestern part of North America and the state of Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific. The country also has five populated and nine unpopulated territories in the Pacific and the Caribbean. At 3.71 million square miles (9.62 million km2) and with around 318 million people, the United States is the world's 3rd or 4th-largest country by total area and third-largest by population. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverseand multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many countries.[19]The geography and climate of the United States is also extremely diverse, and it is home to a wide variety of wildlife.
hungary
Hungary ![]() i/?h????ri/ (Hungarian: Magyarország [?m???rorsa??] (
i/?h????ri/ (Hungarian: Magyarország [?m???rorsa??] (![]() )) is alandlocked country in Central Europe.[7] It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia andCroatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The country's capital and largest city is Budapest. Hungary is a member of the European Union, NATO, the OECD, the Visegrád Group, and the Schengen Area. The official language is Hungarian, which is the most widely spoken non-Indo-Europeanlanguage in Europe.
)) is alandlocked country in Central Europe.[7] It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia andCroatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The country's capital and largest city is Budapest. Hungary is a member of the European Union, NATO, the OECD, the Visegrád Group, and the Schengen Area. The official language is Hungarian, which is the most widely spoken non-Indo-Europeanlanguage in Europe.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins) and also in the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). The human body contains about 3% by mass of nitrogen, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes movement of the element from the air, into thebiosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere.
nitogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element with symbol N and atomic number 7. At room temperature, it is a gas of diatomic molecules and is colorless and odorless. Nitrogen is a common element in the universe, estimated at about seventh in total abundance in ourgalaxy and the Solar System. On Earth, the element is primarily found as the gas molecule; it forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere. The element nitrogen was discovered as a separable component of air, by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford, in 1772.
gold
The last gold certificate and gold coincurrencies were issued in the U.S. in 1932. In Europe, most countries left the gold standard with the start of World War I in 1914 and, with huge war debts, did not return to gold as a medium of exchange. The value of gold is rooted in its medium rarity, easily handling, easy smelting, non-corrosiveness, distinct color and non-reactiveness to other elements; qualities most other metals lack.
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and atomic number 79. It is a bright yellow dense, soft, malleable and ductile metal. The properties remain when exposed to air or water. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements, and is solid under standard conditions. The metal therefore occurs often in free elemental (native) form, as nuggets or grains, in rocks, inveins and in alluvial deposits. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, such as with tellurium as calaverite, sylvanite, or krennerite.
As the metallic native element mineral, gold structurally belongs to the isometric coppergroup. It also forms a solid solution series with the native element silver (Ag) to which it is often naturally alloyed (electrum). Other common natural gold alloys are with copper andpalladium (Pd).
silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (Greek: ??????? árguros, Latin:argentum, both from the Indo-European root *arg- for "grey" or "shining") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it possesses the highest electrical conductivity of any element, the highest thermal conductivity of any metal and is the most reflective metal on the planet. The metal occurs naturally in its pure, free form (native silver), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite andchlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zincrefining.
aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum; see spelling differences) is a chemical element in the boron group with symbol Al and atomic number 13. It is a silvery white, soft, ductile metal. Aluminium is the third most abundant element (after oxygen and silicon), and the most abundant metal in the Earth's crust. It makes up about 8% by weight of the Earth's solid surface. Aluminium metal is so chemically reactive that native specimens are rare and limited to extreme reducing environments. Instead, it is found combined in over 270 different minerals.[5] The chief ore of aluminium is bauxite.